Synonyms in Chinese – Even Within the Same Word!

Word Structure: Parallel 并列式
Compound Words – Multiple Morpheme Words (合成词)
This is part 4 of an 8-part series exploring all 7 types of Chinese compound words. This is part 4 – Synonyms in Chinese. Click below for the other parts:
Part 1 – Part 2 – Part 3 – Part 4 – Part 5 – Part 6 – Part 7 – Part 8
Parallel 并列式
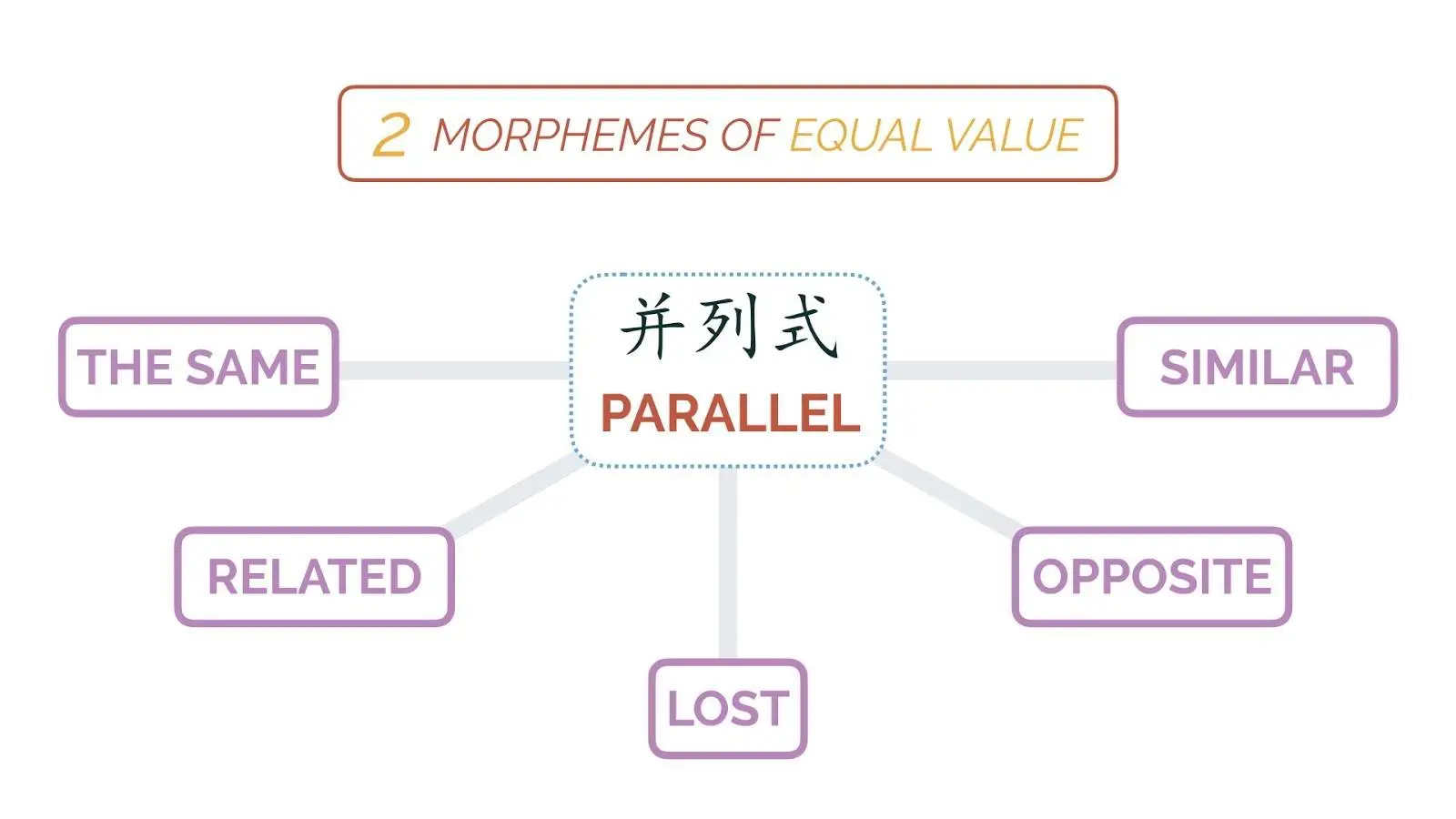
The two morphemes in a Parallel word have equal value. The meaning of the two morphemes can be the same (相同), nearly the same (相近), opposite (相反), related to the same concept (相关), or one of the two morpheme’s meaning has disappeared (消失).
Exactly the Same & Nearly the Same
(相同和相近) – Synonyms in Chinese
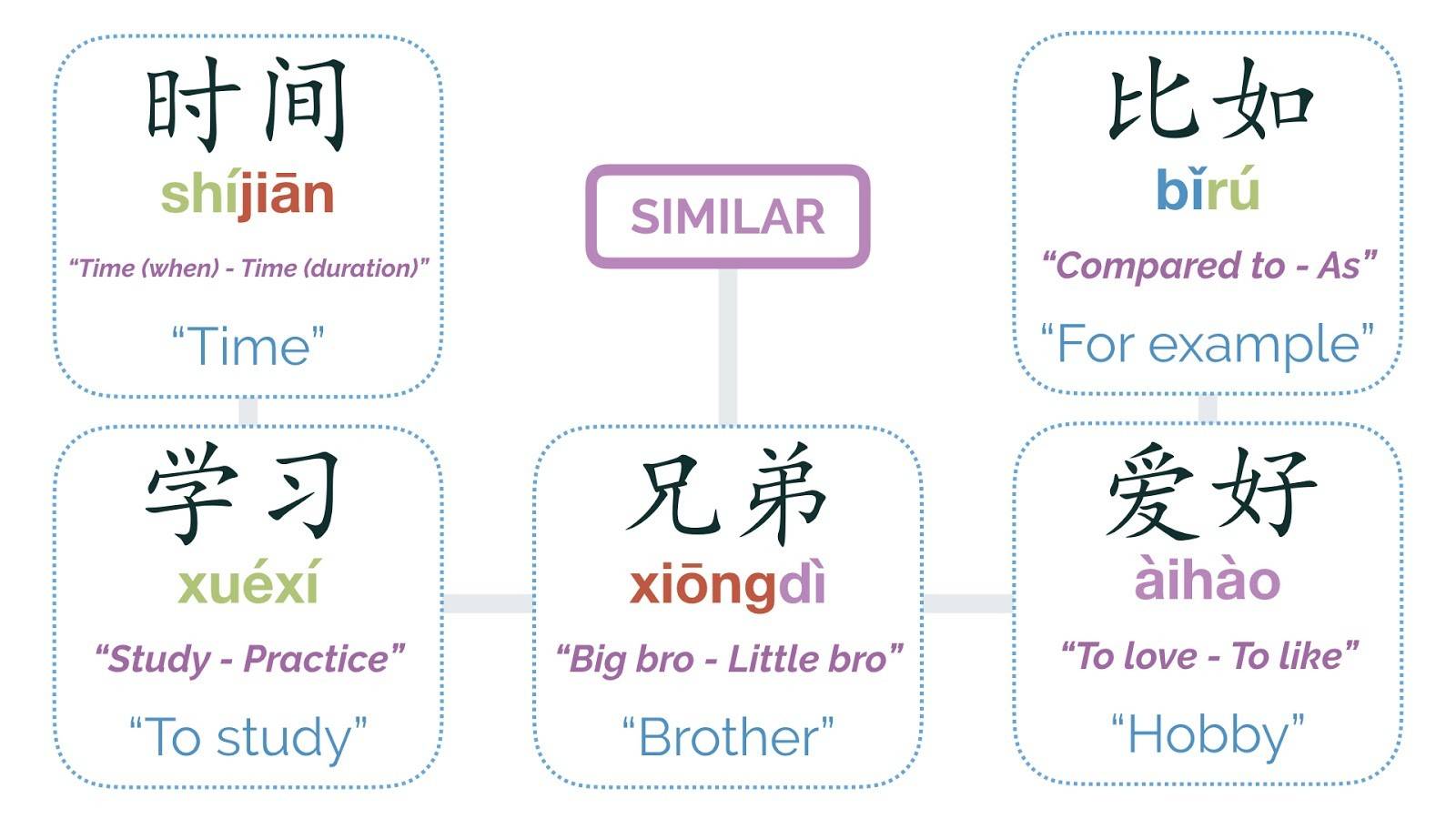
朋友 péngyǒu
Friend. Both 朋 and 友 have the meaning of “friend.”
兄弟 xiōngdì
Brother or Brothers. Both 兄 and 弟 have the meaning of “brother.”
灰尘 huīchén
Dust, both 灰 and 尘 have the meaning of “dust.”
Further Examples of Synonyms in Chinese:
真正 zhēnzhèng
Genuine
江河 jiānghé
River
均匀 jūnyún
Even, Well Distributed
道路 dàolù
Road
离别 líbíe
Part (for a longish period); Bid Farewell
答应 dáyìng
To Promise
依靠 yīkào
To Rely On
如同 rútóng
As, Like
爱好 àihào
Hobby
伟大 wéidà
Great, Mighty (as in a person’s ability or influence)
孤独 gūdú
Alone, Isolated
寒冷 hánlěng
Bitterly Cold
美丽 měilì
Beautiful
富裕 fùyù
Rich, Wealthy
Opposite (相反)
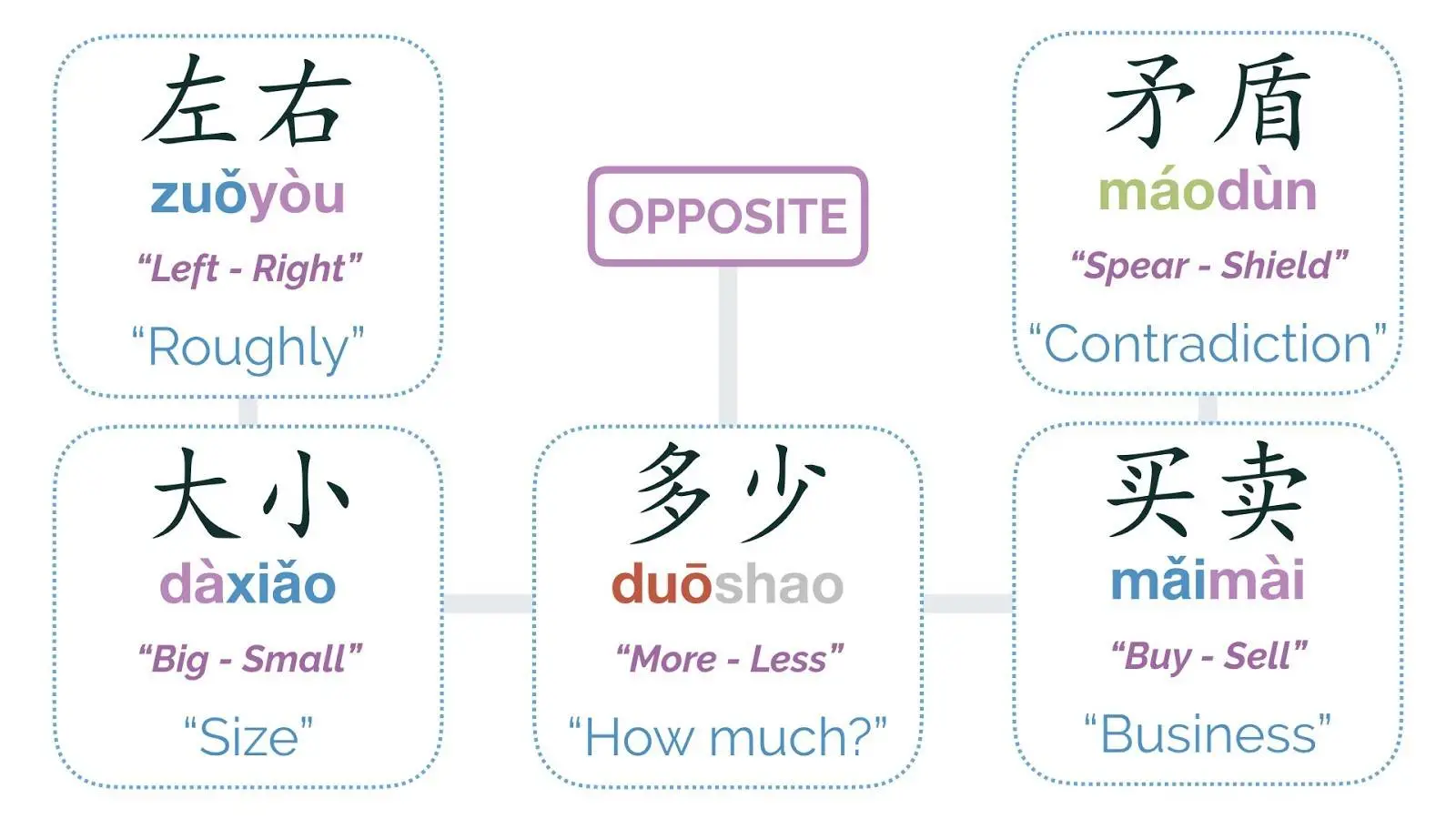
左右 zuǒyòu
Approximately or On Both Sides
Left 左 and Right 右 are opposite
进出 jìnchū
To Pass In & Out
Enter 进, and Exit 出 are opposite
多少 duōshao
How Much? or Some Amount
Many 多 and Few 少 are opposite
Further Examples of Opposite Juxtaposition 相反并列式:
父母 fùmǔ
Mother & Father
内外 nèiwài
Internal & External
上下 shàngxià
Above & Below
儿女 érnǚ
Sons & Daughters
子女 zínǚ
Sons & Daughters
黑白 hēibǎi
Black & White
大小 dàxiǎo
Size (like shoe size)
长短 chángduǎn
Length (long & short)
开关 kāiguān
Light Switch (open & close)
买卖- mǎimài
Do Business (buy & sell)
东西- dōngxī
Stuff (east & west)
出入- chūrù
Come In & Go Out (exit & enter)
来往- láiwǎng
(regarding human relationships) Come & Go (come & go)
得失 déshī
Success & failure (gain & lose)
生死 shēngsǐ
Life & Death (life & death)
呼吸 hūxī
Breath (exhale & inhale)
高低 gāodī
Height (high & low)
深浅 shēnqiǎn
Depth (deep & shallow)
反正 fǎnzhèng
In any case, anyway (against & for)
横竖 héngshù
In any case, anyway (horizontal & vertical)
迟早 chízǎo
eventually, sooner or later (late & early)
早晚 záowǎn
sooner or later (early & late)
先后 xiānhòu
being early or later: priority (beginning & end)
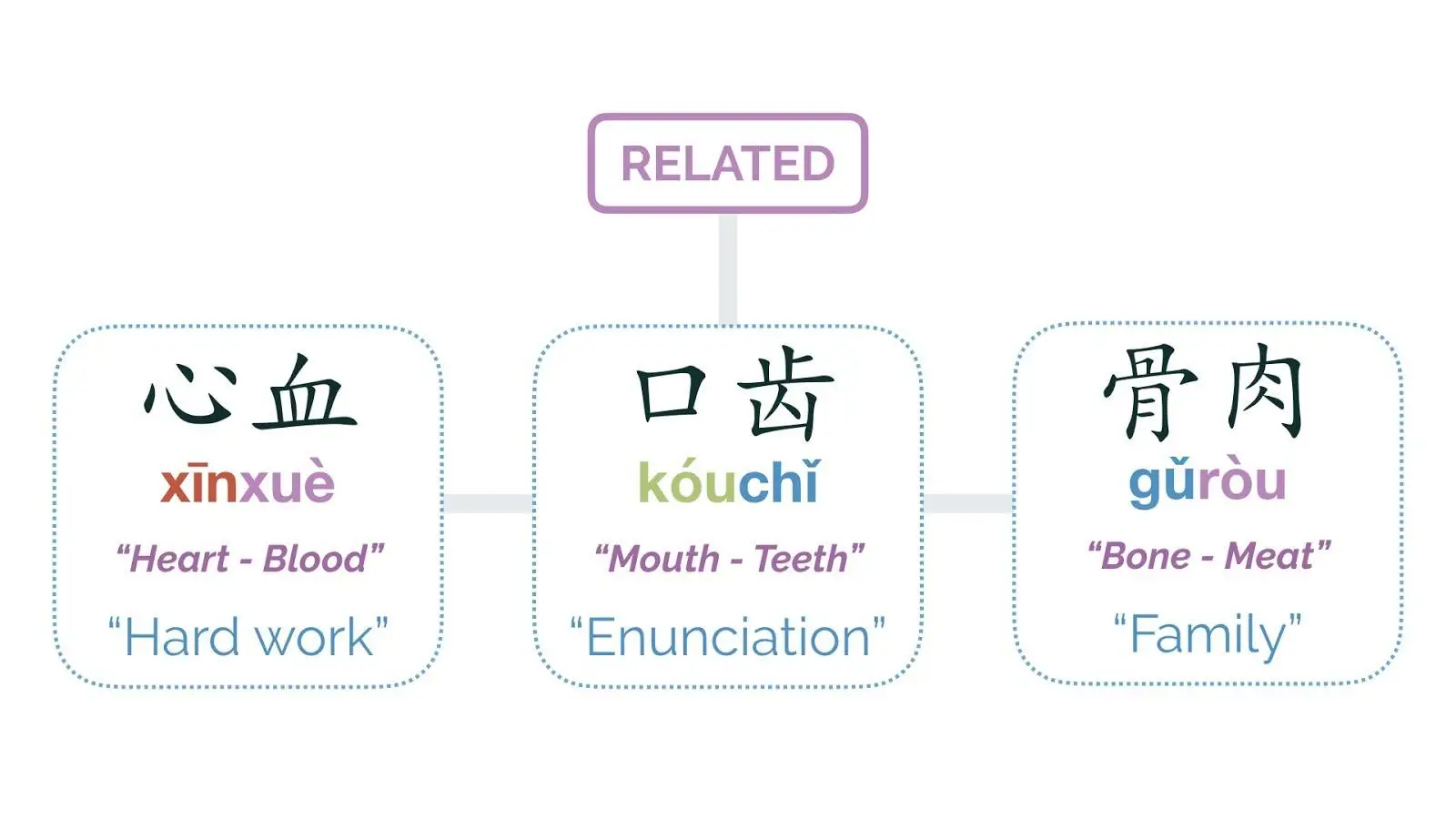
These words contain two morphemes that come from the same type of thing, but they aren’t the same. Also, worth noting that many of these are not a direct translation of the two morphemes’ original meaning. For example, 骨肉 gǔròu is made up of “bone” 骨 and “meat” 肉,but the definition is one’s children, parents, brothers, sisters or other blood relatives, not only bones and meat.
Examples for those Chinese synonyms:
中西 zhōngxī,中外 zhōngwài
中西 refers to the relationship between China (中) and the West (西). 中外 refers to the relationship between China (中) and any foreign country (外). These morphemes are not the same or opposites. However, they are in the same category of things (states and political entities).
母女 múnǚ
The relationship between a mother and daughter. Not the same or opposites, but in the same category (relations)
江湖 jiānghú
江 means river and 湖 lake, but the word 江湖 refers to all corners of the earth, so its an excellent example of a Parallel Related word where the meaning is only abstractly related to the morphemes.
Further Examples for Synonyms in Chinese:
母子 múzǐ
Mother & Son Relationship
父女 fùnǚ
Father & Daughter Relationship
父子 fùzǐ
Father & Song Relationship
骨肉 gǔròu
Blood relative(s) (bone & meat)
手足 shǒuzú
Movement or Brothers (hand & foot)
眉目 méimù
progress, the prospect of a solution (eyebrow & eye)
口齿 kóuchǐ
enunciation; ability to speak (mouth & teeth)
江山- jiāngshān
Country or State Power (river & mountain)
耳目- ěrmù
One who spies for somebody else (ear & eye)
领袖- lǐngxiù
Leader (of people) (collar & sleeve)
手脚- shóujiǎo
Movement of limbs (hand & foot)
嘴脸- zuíliǎn
somebodies ugly features or face (mouth & face)
口舌- kǒushé
dispute or misunderstanding caused by gossip (mouth & tongue)
心血- xīnxuè
painstaking care or effort (heart & blood)
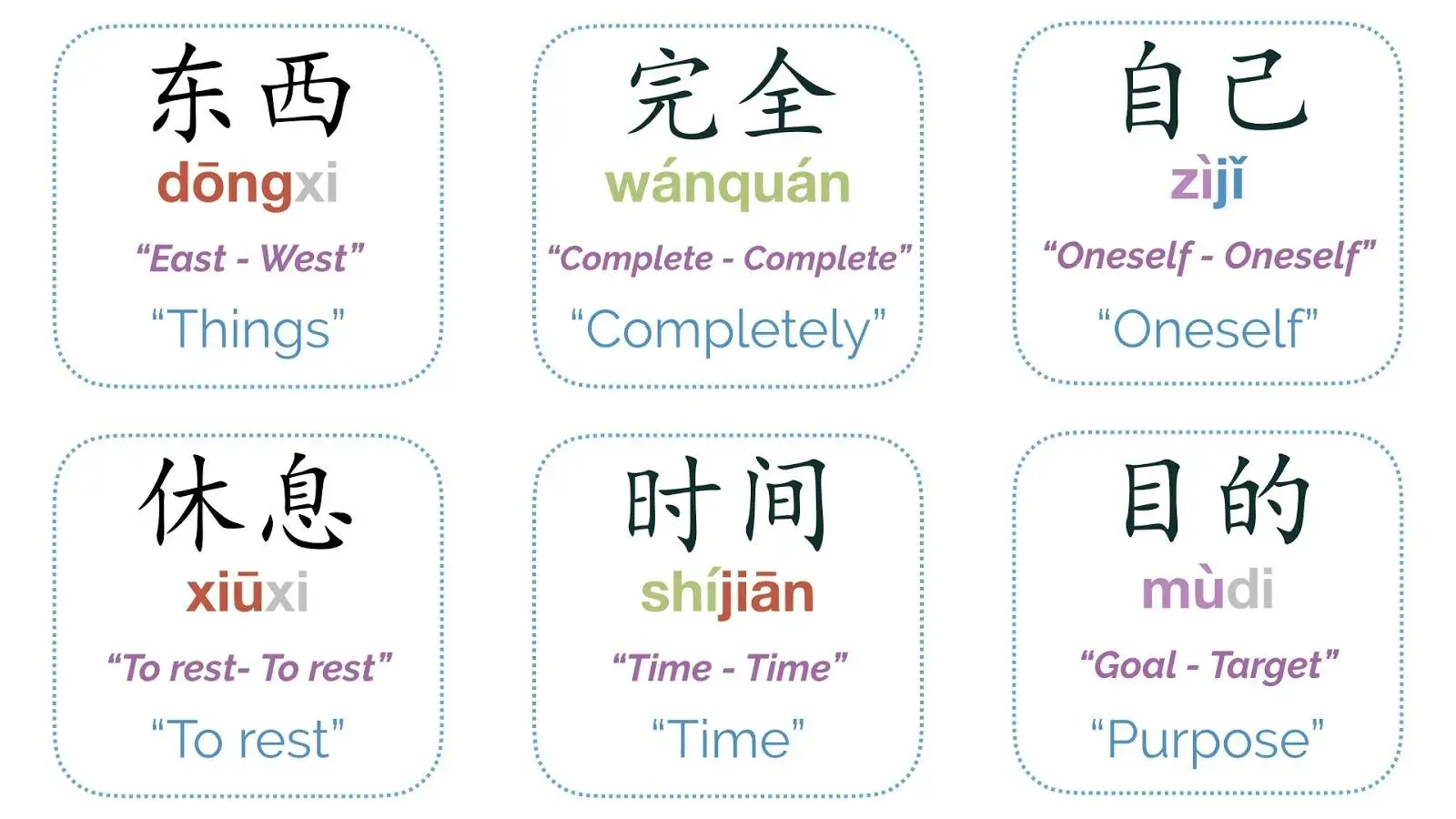
One Meaning Disappears (消失)– Synonyms in Chinese
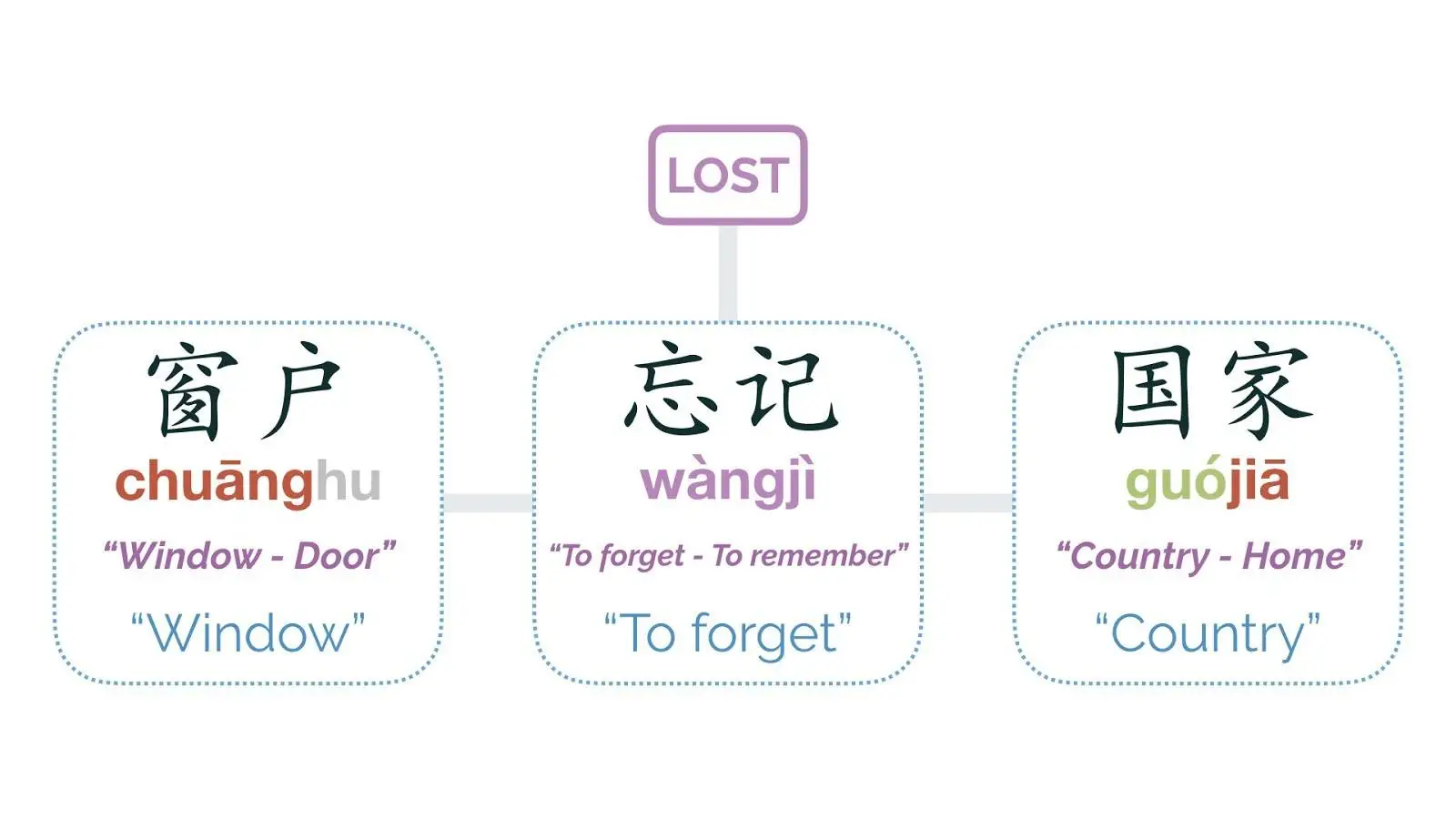
Some words have two morphemes, but one of the morphemes no longer expresses any meaning (it may have at some point in the history of Chinese, but in modern Chinese has disappeared.)
Examples:
忘记 wàngjì
To Forget- (forget & remember, remember’s 记 meaning has disappeared)
国家 guójiā
Country (country & home, home’s 家 meaning has disappeared)
人物 rénwù
Person (person & thing, thing’s 物 meaning has disappeared)
窗户 chuānghu
Window (window & door, door’s 户 meaning has disappeared)
甘苦 gānkǔ
Hardships & difficulties experienced in work (sweet & bitter, sweet/s 甘 meaning has disappeared)
好歹 háodǎi
Mishap; disaster- (good & evil, good’s 好 meaning has disappeared)
是非 shìfēi
Quarrel; Dispute- (is & is not, is’ 是 meaning has disappeared)
So now you know more about synonyms in Chinese. Check out the rest of the series to learn even more.








